How to Analyze Real Estate Investments Like a Pro: A Step-by-Step Guide
Share
Real estate investing is one of the most powerful ways to build long-term wealth — but only if you know how to analyze a property the right way. Whether you’re buying your first rental property or scaling a real estate portfolio, learning how to perform a real estate investment analysis is the key to identifying profitable opportunities, minimizing risk, and making data-driven decisions.
This step-by-step guide will show you how to evaluate a property like a professional investor — from setting clear goals to running the numbers and projecting future returns.
Step 1: Define Your Real Estate Investment Strategy
Before diving into calculations, get clear on your goals. Are you investing for cash flow, capital appreciation, or quick profits through flipping?
Your strategy determines which metrics matter most:
- Buy-and-hold investors focus on consistent rental income and long-term growth.
- Fix-and-flip investors prioritize renovation costs, resale value, and time on market.
- Short-term rental investors evaluate occupancy rates and local tourism demand.
Defining your goals also helps you choose the right financing structure, location, and property type — whether that’s a single-family home, multifamily building, or commercial space.
Step 2: Research the Market
A great deal on a bad street is still a bad deal. Professional investors always start with market analysis before crunching any numbers.
Look for:
- Job growth and population trends — steady employment attracts long-term tenants.
- Rental demand — check vacancy rates and average rental prices.
- Economic stability — avoid overly dependent “one-industry” towns.
- Infrastructure development — new transport links, schools, or shopping centers can increase property values.
Websites like Zillow, Redfin, or local government portals provide valuable market data. If you invest internationally, research taxes, landlord regulations, and currency risks.
Step 3: Estimate Income Potential
Next, calculate how much money the property can make.
Start with gross rental income — the total rent you expect to collect each year. Use comparable rentals in the same area (“comps”) to estimate realistic numbers. Don’t forget to include additional income sources such as parking fees, laundry, or storage.
Then calculate effective rental income by accounting for potential vacancies. A 5–10% vacancy allowance is common in most markets.
Example:
If monthly rent = €1,500
Annual rent = €18,000
Assume 5% vacancy → €18,000 × 0.95 = €17,100 effective income
Step 4: Estimate Operating Expenses
Even profitable rentals can drain cash if expenses are underestimated. Typical operating costs include:
- Property taxes
- Insurance
- Maintenance & repairs
- Property management fees
- Utilities (if paid by owner)
- HOA or condominium fees
- Advertising and legal costs
A simple rule of thumb: operating expenses often total 35%–50% of rental income.
Subtracting these from your effective income gives your Net Operating Income (NOI) — a critical number for calculating profitability.
Formula:
👉 NOI = Effective Income – Operating Expenses
Step 5: Calculate Key Investment Metrics
Now it’s time for the fun part — the numbers that tell you whether a property is a good deal.
1. Cap Rate (Capitalization Rate)
Cap rate measures how much return you’ll earn if you paid cash for the property.
Formula:
👉 Cap Rate = (NOI ÷ Purchase Price) × 100
A higher cap rate usually means a better return — but it can also mean higher risk.
2. Cash-on-Cash Return
If you finance the property, this metric shows your actual return on invested cash.
Formula:
👉 Cash-on-Cash Return = (Annual Cash Flow ÷ Cash Invested) × 100
3. ROI (Return on Investment)
ROI gives a big-picture view of profitability over time.
Formula:
👉 ROI = (Net Profit ÷ Total Investment) × 100
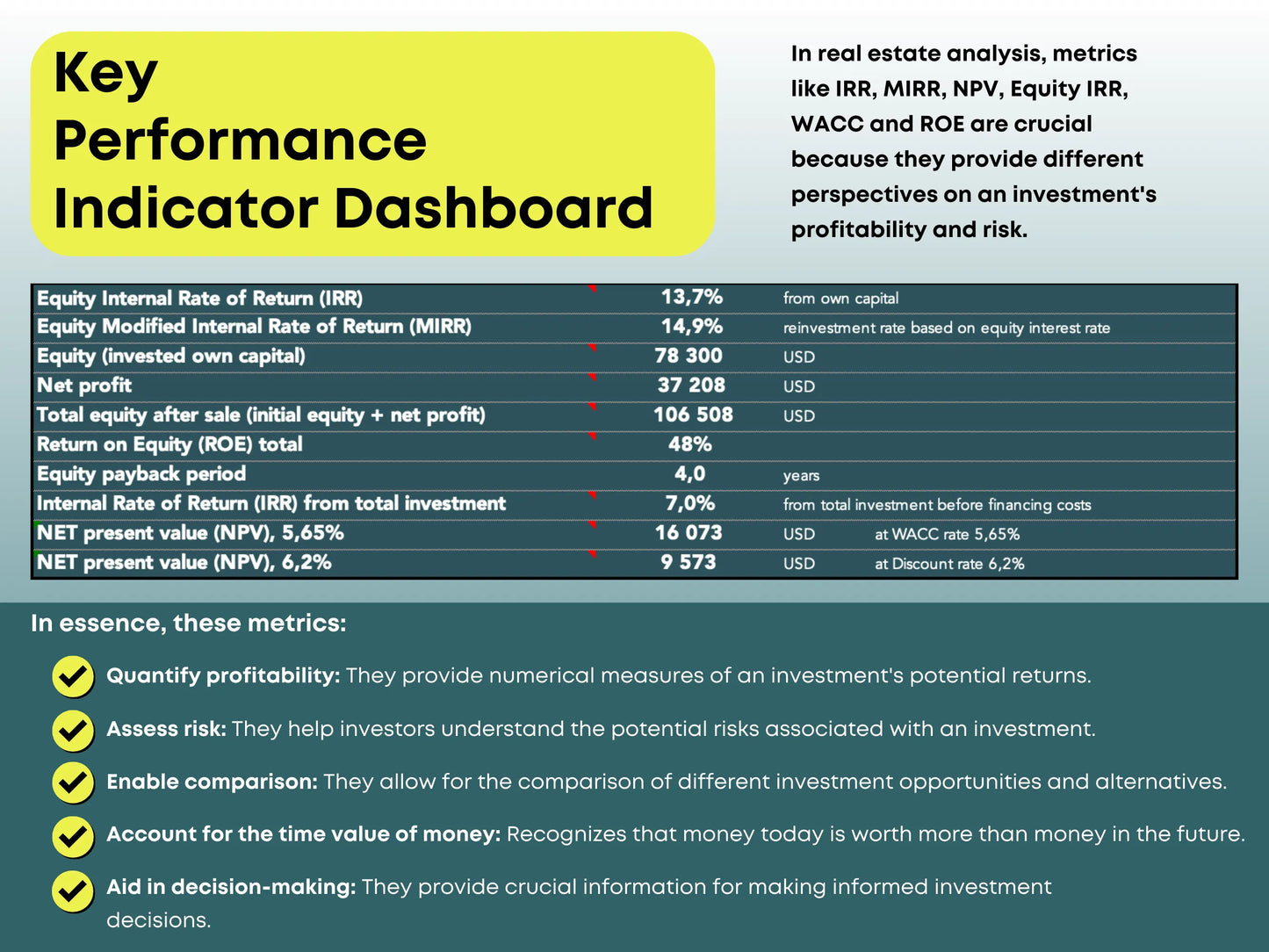
4. ROE (Return on Equity)
ROE (Return on Equity) measures how much profit you earn based on your initial invested equity, not the property’s total cost.
Formula:
👉 ROE = Total Returns / Initial Invested Equity × 100
5. IRR (Internal Rate of Return)
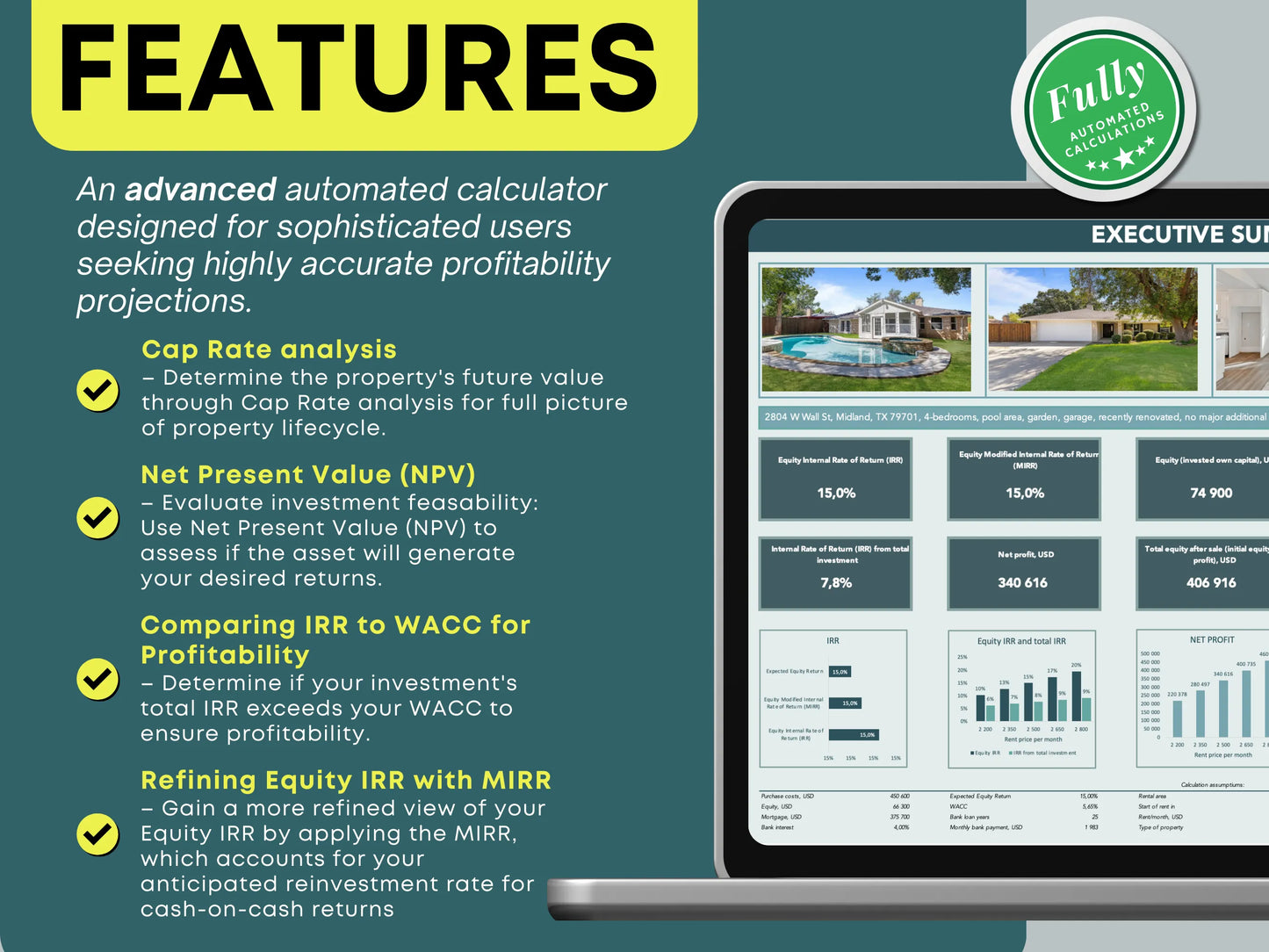
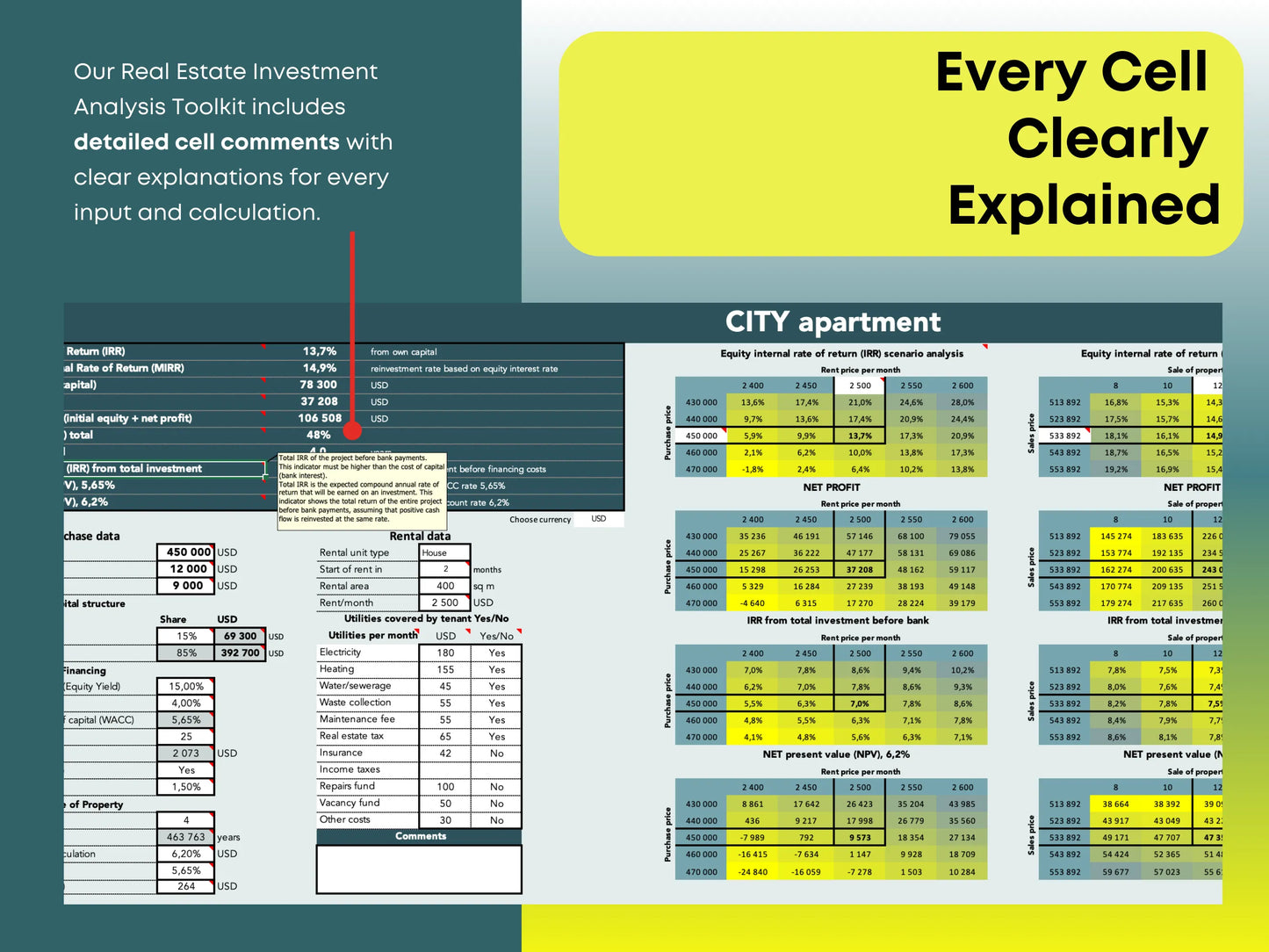
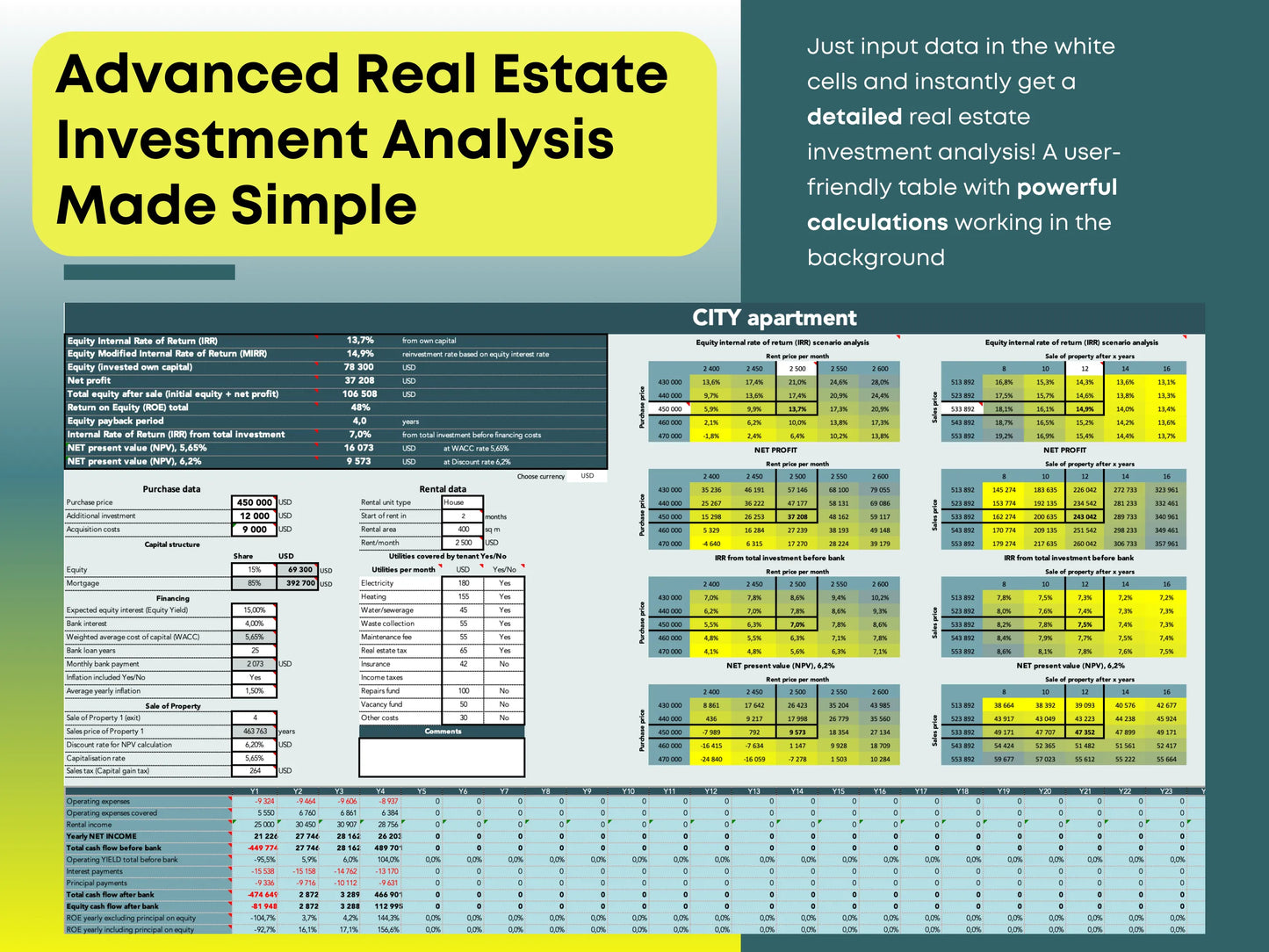
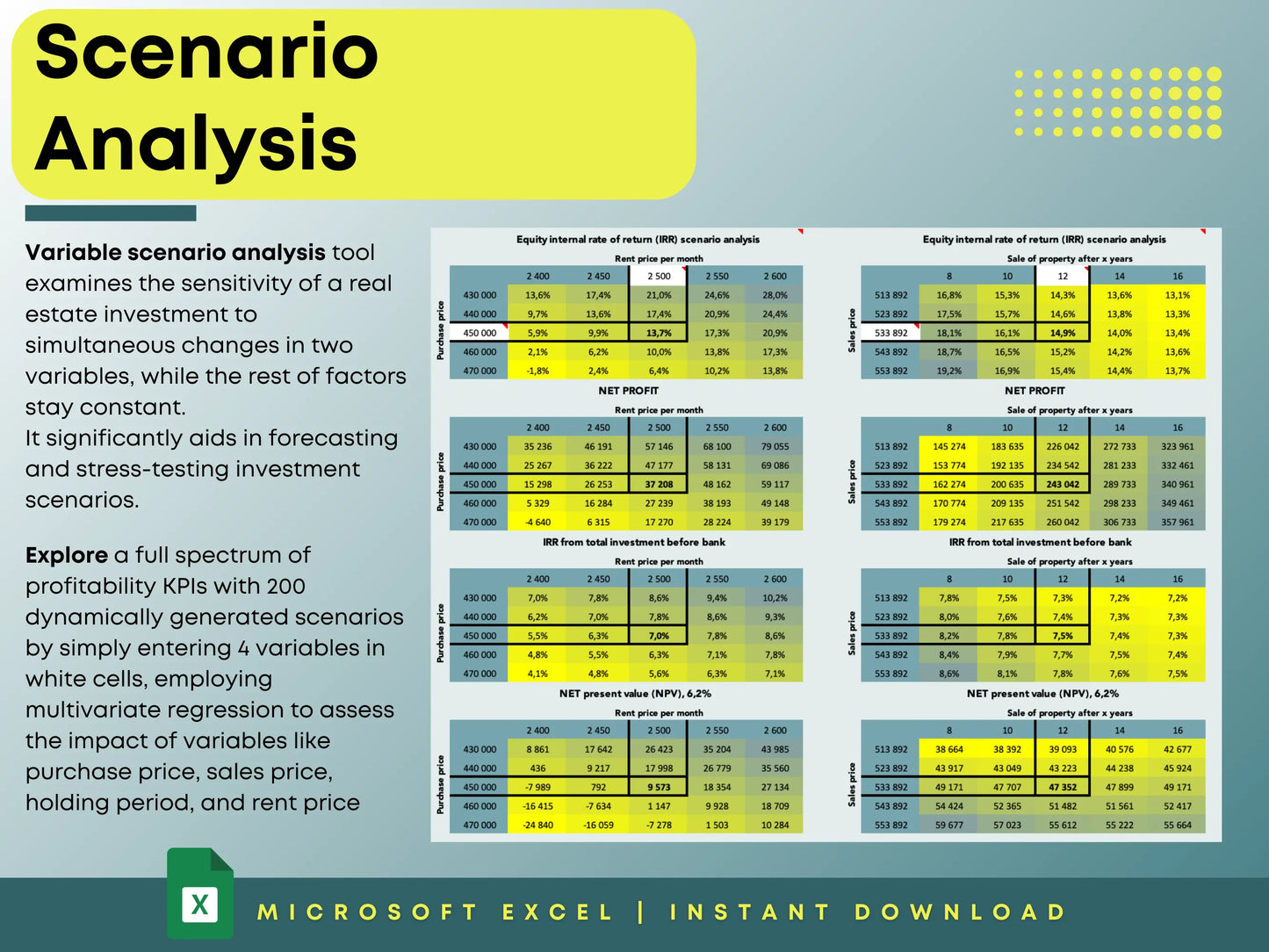
IRR measures the total profitability of an investment across multiple years — factoring in cash flow, appreciation, and time value of money. Many professionals use spreadsheets or tools like our Real Estate Profitability Calculator to calculate IRR automatically.
Step 6: Analyze Financing Scenarios
Financing can make or break a deal. Compare different loan options to see how interest rates and down payments affect your returns.
For example:
- Lower down payment = higher leverage but higher risk
- Longer loan term = lower monthly payments but higher total interest
Use spreadsheets or tools to test multiple financing methods (like all-cash, conventional loan, or interest-only) and see which gives the best cash flow and return on equity (ROE).
Step 7: Account for Future Growth
Professional investors don’t just look at today’s numbers — they project future performance.
Model your investment over 5–10 years by estimating:
- Annual rent growth (2–3%)
- Expense inflation (1–2%)
- Property appreciation (2–5%)
- Potential refinancing or sale value
This forward-looking approach helps you see long-term ROI and ensures your assumptions stay realistic. You can easily test different outcomes using real estate sensitivity analysis spreadsheets.
SEO keywords: real estate appreciation, property forecast, long term real estate investment, rental growth projection.
Step 8: Perform Comparative Market Analysis (CMA)
Comparing your target property to similar ones recently sold or rented nearby helps confirm your assumptions.
Check:
- Recent sale prices (within last 6–12 months)
- Current rental rates for similar size and condition
- Days on market
- Average occupancy rate
A good CMA ensures you’re not overpaying and that your rent expectations are aligned with reality.
Step 9: Calculate Your Offer Price
Once you’ve run all the numbers, decide how much you’re willing to pay. Build a margin of safety by using conservative estimates — assume slightly higher expenses, longer vacancies, and lower rent growth.
For example, if your analysis shows a 9% cap rate under ideal conditions, budget for 7–8% to stay safe. This approach keeps you profitable even if things don’t go perfectly.
If the seller’s price doesn’t align with your calculated value, negotiate — or walk away. There will always be another deal.
Step 10: Review and Monitor Performance
Even after purchase, your job isn’t done. Great investors continually analyze property performance to ensure returns stay on target.
Track metrics such as:
- Monthly cash flow
- Vacancy rate
- Maintenance costs
- Market rent growth
- Return on equity (ROE) over time
Consider refinancing or selling if your equity grows faster than your cash flow. Data-driven adjustments help keep your portfolio performing like a professional’s.
Final Thoughts
Learning how to analyze real estate investments like a pro takes time — but once you master it, you’ll never look at property the same way again. You’ll recognize good deals instantly, avoid costly mistakes, and build a portfolio that grows your wealth safely and sustainably.
Use the formulas, checklists, and calculators discussed here to make data-backed decisions instead of emotional ones. Whether you’re analyzing your first rental property or expanding into multifamily deals, the foundation is the same: know your numbers, verify your assumptions, and plan for the long term.
💡 Bonus Tip
Try a Real Estate Investment Profitability Calculator Pro version to instantly compare multiple financing methods, analyze ROE, ROI, IRR, and cash flow — and see which deal performs best. It’s the easiest way to analyze real estate like a true professional.
Or try our https://whereisthemoney.shop/products/real-estate-investment-calculator-bundle to quickly identify your top property opportunities — then dive deeper with the Pro Investment Calculator to test which financing method creates the most value.